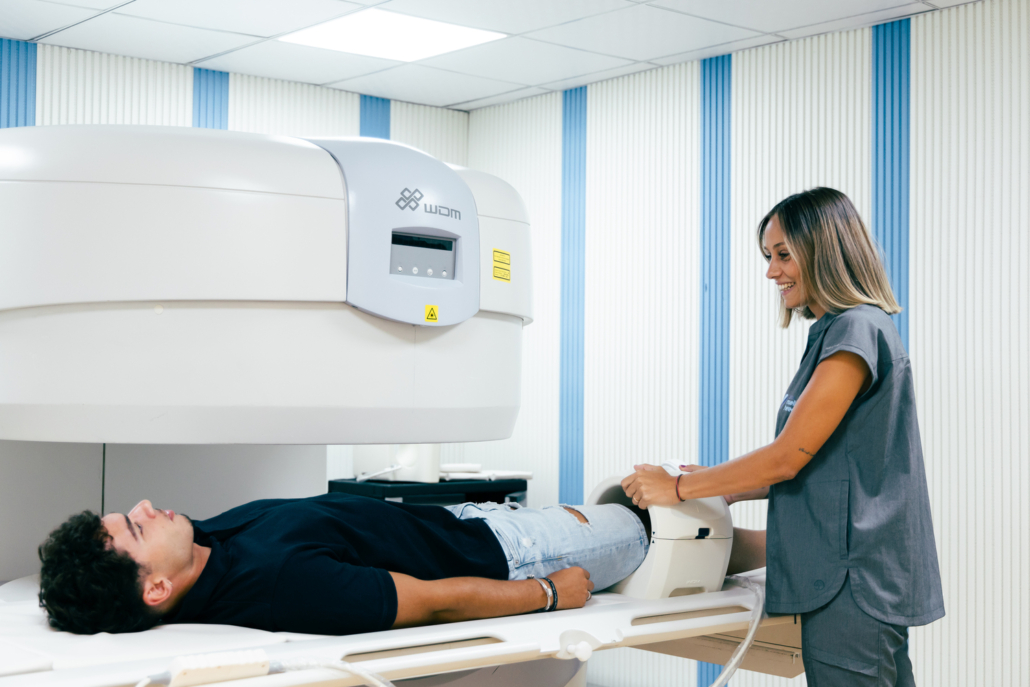
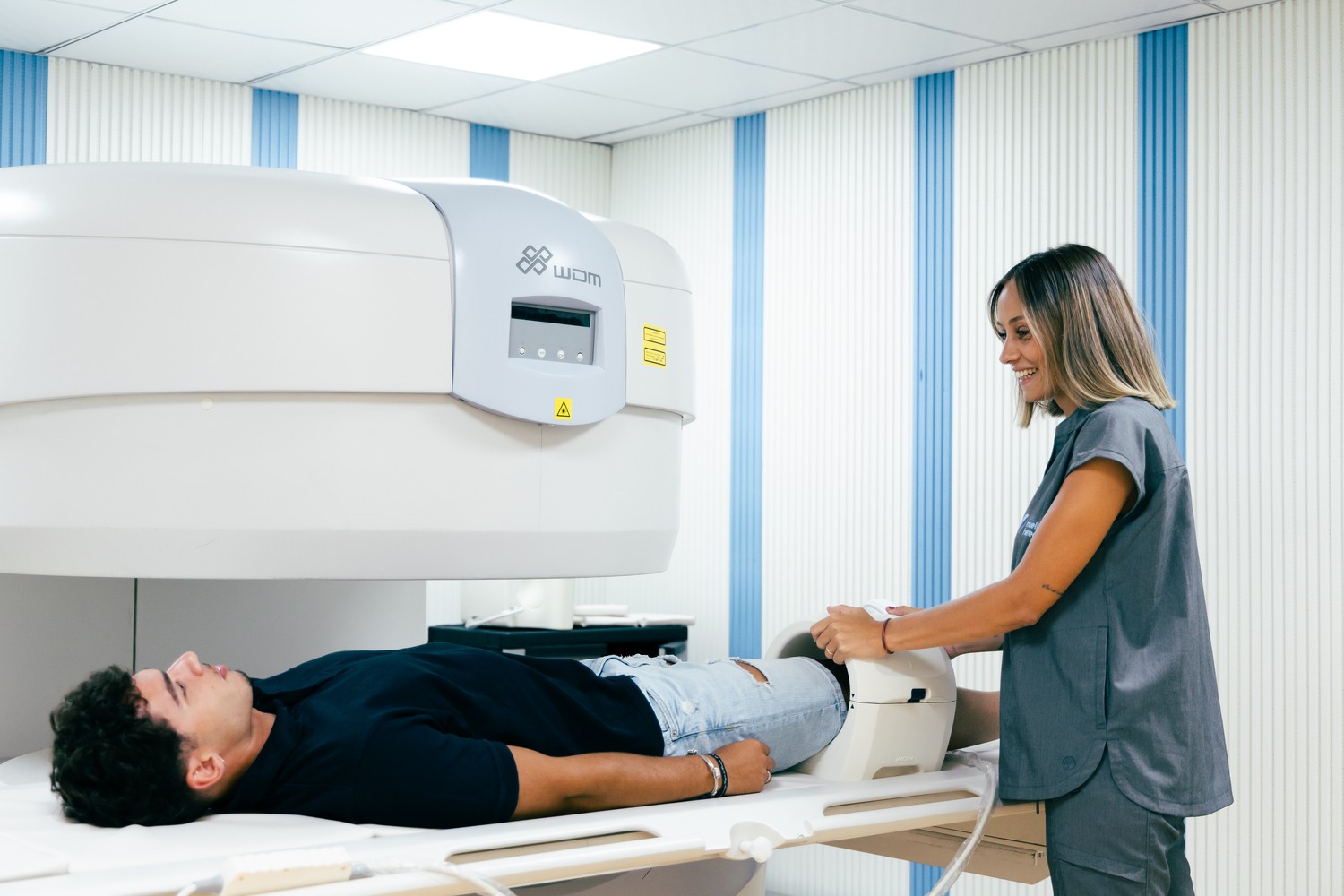
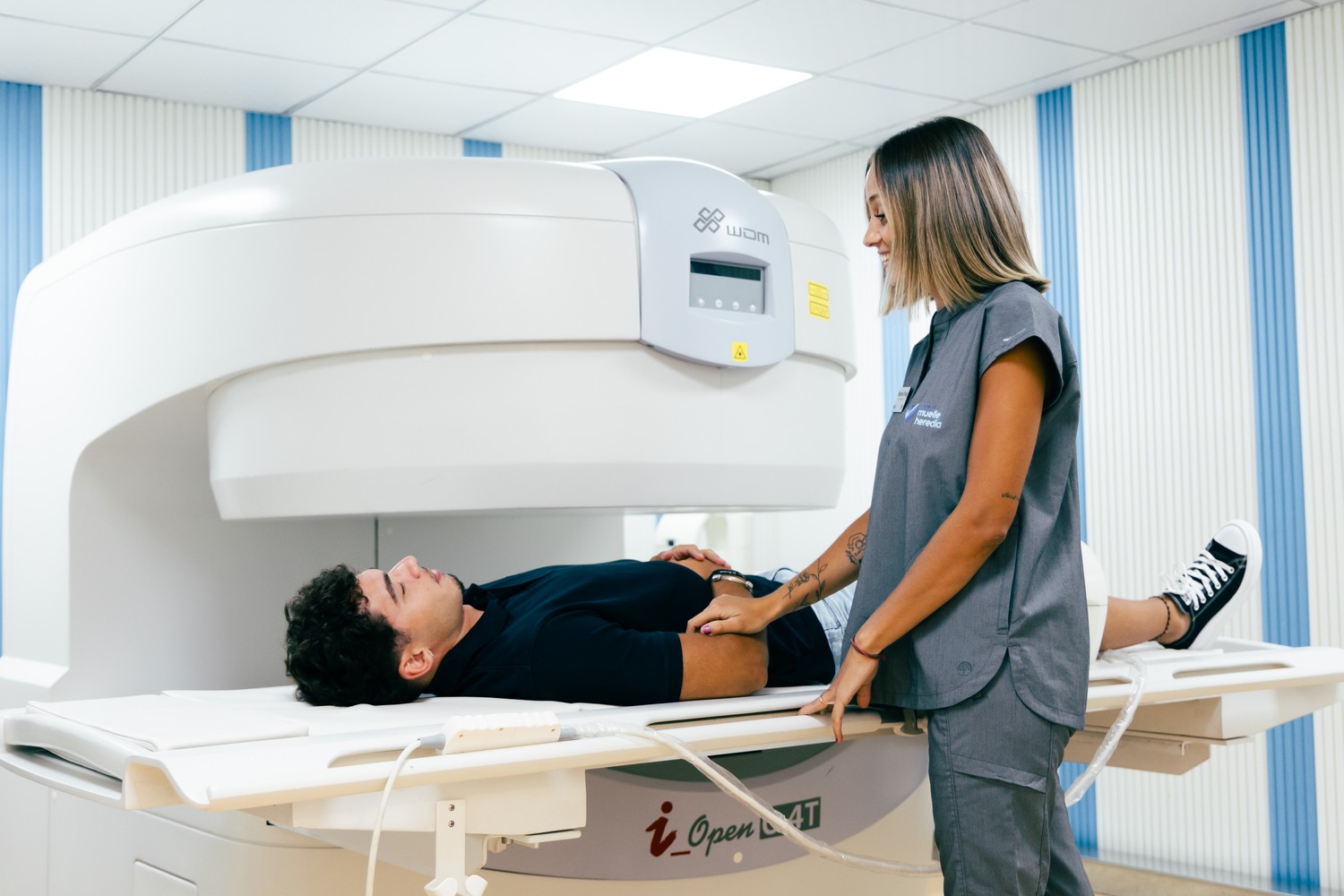
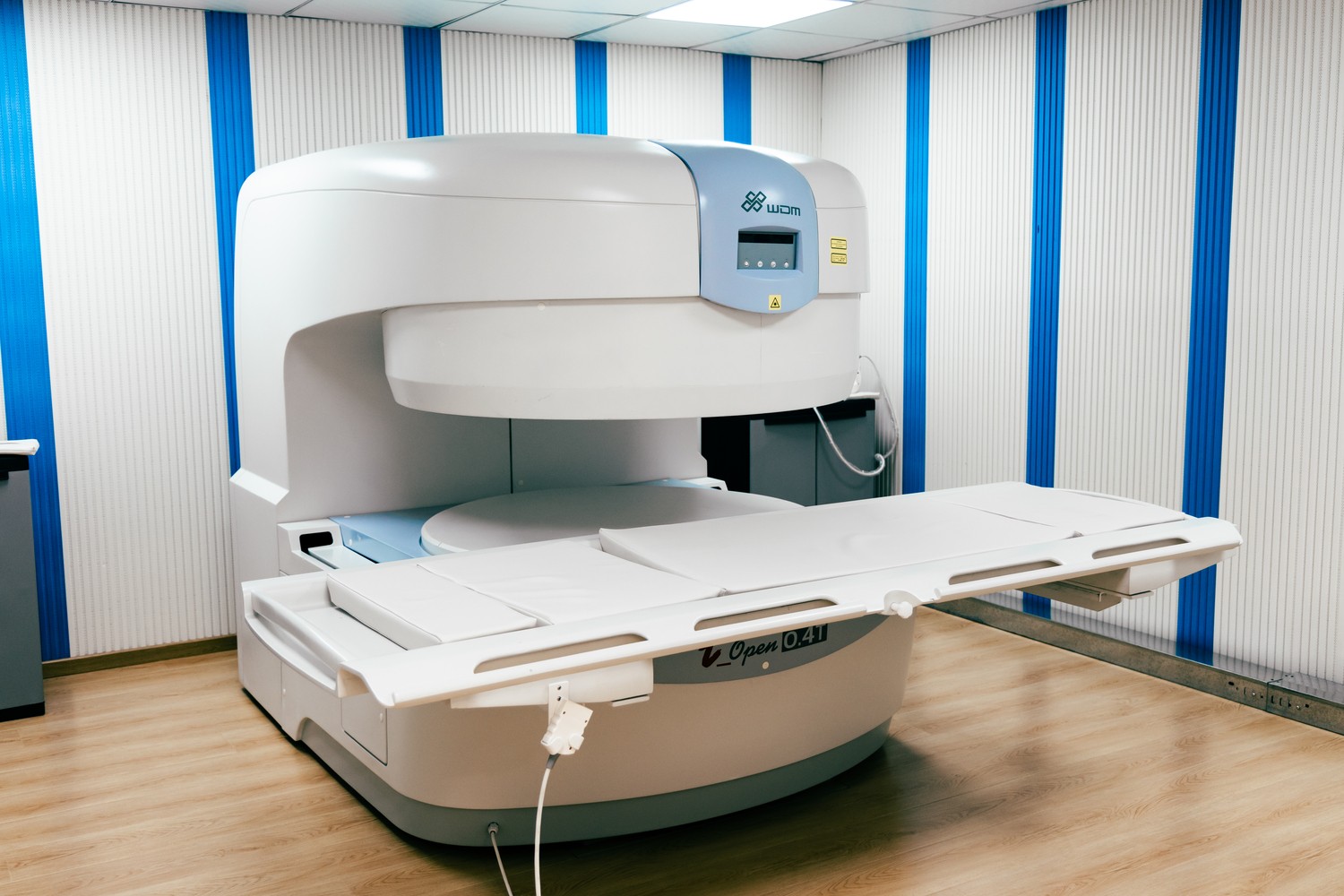
Get an accurate and comfortable diagnosis now, without claustrophobia.
Quick appointments and personalized attention!

También destaco la facildad y rapidez en concretar cita, y la conveniencia de tener los resultados disponibles en plataforma online dentro de pocos días. Precio muy razonable ademas. Regreso para cualquier resonancia que tengo que realizar. Gracias.
Tienen una disponibilidad de resonancia relativamente rápida, pero pronto comprendes por qué. En primer lugar, en mi caso su máquina no mostró adecuadamente la persistencia de un edema óseo (que estaba si presente y se puso de relieve la semana siguiente en una resonancia magnética realizada en otro centro). En segundo lugar, el radiólogo del centro habló en el informe de la desaparición completa de un edema que un traumatólogo, en cambio destacó al día siguiente expresando ademàs que las imagenes eran de mala calidad de todas maneras. Y, en tercer lugar, el establecimiento no sólo, ante las evidencias, no reembolsó el servicio sino que además se negó a reembolsar el complemento de 50 euros por la urgencia, a pesar de que el informe había cambiado de un día para otro. Lamento decir que, en mi opinión y en la de los médicos que he consultado, si quieres tener imágenes de calidad y un diagnóstico correcto es mejor acudir a otro lado.
UPDATED despues de la contestaciòn de la clinica: en el otro centro no llegaran a la misma conclusion simplemente porque con máquinas mejores si han visto claramente el edema mientras la vuestra no. Y yo no impulsè a nadie, que sea claro, el radiólogo vuestro cambiò el informe despues que un traumatologo de otro centro dijo que el informe no era 100% corecto.
Destaco la amabilidad y profesionalidad del personal por el trato recibido.
Muchas gracias!!!
Totalmente recomendable. 10
María me ayudó a mantener la calma durante la resonancia ya que estaba muy nerviosa. Sin duda recomendaría la clínica! Gracias por todo!
Felicitaciones a todos los que colaboran para que este lugar funciones tan bien porque lo han logrado!!!
El ticket que dan para el “parking gratuito” no valida por el retraso que llevan y tenemos que pagarlo. Nos entregan la resonancia en pen y se equivocan, me han dado una que no es la mía lo que me hace ir de nuevo hasta la clínica exclusivamente a recoger mi prueba porque se han equivocado, el trato a la hora de la resonancia con la enfermera genial
Todo perfecto.
y sobre todo también, un trato muy humano. Gracias
Muchas gracias
Muy bien atendido e informado.
Muy cómodo en la prueba diagnóstica.
Muchas gracias.
Muy contenta con la experiencia.
Recomendado 100%
Personal muy atento y amable.
Servicio y profesionalidad estupendos.
Cuando vine aquí me atendió Lola y Maria es muy simpática y sabe como hacer que te relaje
La máquina es abierta me metieron de lado la cabeza todo el tiempo la tuve fuera y aguante los 20 min que duro la lumbar sin duda para mi si tengo que repetir otra no buscaré otro sitio
Muy agradecido
Mi madre iba con poca movilidad y María ha sido muy amable y profesional ayudándola en todo.
El diagnóstico nos lo han dado rapidísimo.
Sitio super recomendable, un puntazo tener parking gratis.
Gracias por todo.
Resultado de las pruebas al momento de finalizar.
Desde la gestión de la cita a acabar un trato e información de 10.
¿Where are We?
📍 Calle Real, nº5, El Palo (Málaga Este)
Our MRIs
✅ Fingers
✅ Hand
✅ Wrist
✅ Forearm
✅ Elbow
✅ Humerus
✅ Shoulder
✅ Head
✅ Cervical
✅ Dorsal
✅ Lumbar
✅ Sacrum/Coccyx/Iliac
✅ Pelvis
✅ Hip
✅ Leg
✅ Knee
✅ Tibia
✅ Ankle
✅ Foot
✅ Paranasal sinuses
What is it
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a medical diagnostic technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to obtain detailed images of the inside of the human body. It is a non-invasive tool that allows visualization of anatomical structures and evaluation of the function of organs and tissues.
What are its functions
MRI is especially useful for diagnosing and evaluating a wide variety of medical conditions, such as brain injuries, heart diseases, musculoskeletal disorders, nervous system diseases, tumors, vascular diseases, among others. Additionally, MRI does not use ionizing radiation, making it a safe option for many patients.
Its benefits
- Detailed and accurate images: MRI provides high-resolution, high-contrast images, allowing doctors to clearly visualize the internal structures of the body. This aids in diagnosing various diseases and medical conditions.
- Does not use ionizing radiation: Unlike other imaging techniques, such as X-rays or computed tomography (CT), MRI does not use ionizing radiation. Instead, it relies on magnetic fields and radio waves, making it safer in terms of radiation exposure, especially for patients who require frequent scans or are sensitive to radiation, such as pregnant women or children.
- Soft tissue evaluation: MRI is particularly useful for evaluating soft tissues, such as internal organs, muscles, tendons, and blood vessels. This allows for the detection and diagnosis of a wide range of conditions, such as tumors, injuries, inflammation, and musculoskeletal disorders.
- Functional assessment: In addition to providing anatomical images, MRI can also evaluate the function of certain organs and tissues. For example, functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) is used to map brain activity and assist in the research of specific brain functions.
- Versatility: MRI is a versatile technique that can be used in different areas of the body, such as the brain, heart, spine, joints, abdomen, and pelvis. This makes it a widely applicable tool in various medical specialties.
- Non-invasive: MRI is a non-invasive procedure that does not require surgery or incisions. Although the patient must remain still during the scan, it does not involve any painful or invasive procedures.
Our Advantages
✅ The best price
✅ Fast results in 72 hours.
✅ Express services in 7 hours.
✅ Get your test done in less than 48 hours.
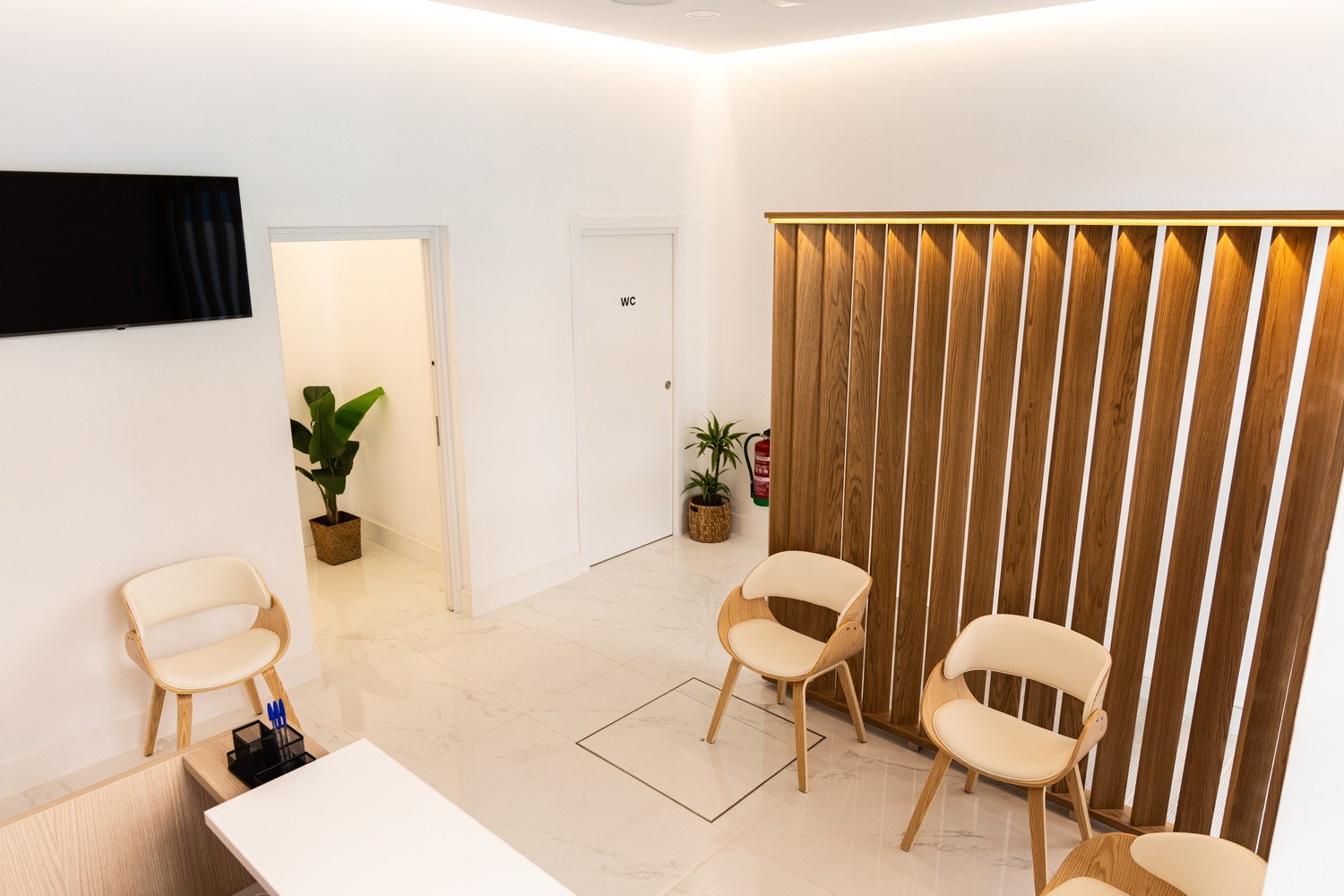
✅ Free parking for 1 hour, 2 minutes from the facility.
✅ Top-quality facilities.
✅ Bus stop next to our facility (Lines 3, 8, 11, and 1)
Are you afraid of claustrophobia during an MRI?
We have the perfect solution for you!
At our center, we offer open MRIs that ensure your comfort and peace of mind. With our state-of-the-art equipment, you can:
✔️ Enjoy an experience without the feeling of confinement.
✔️ Feel relaxed and safe throughout the procedure.
✔️ Get high-quality images without sacrificing your well-being.
✔️ Say goodbye to claustrophobia and hello to a more comfortable and accessible MRI!
Frequent Questions
What is magnetic resonance imaging and what is it used for?
Magnetic resonance imaging is an imaging technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of the body’s organs and tissues, aiding in the diagnosis of various medical conditions.
What is an Open MRI?
Open MRI is a diagnostic imaging technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of the body’s organs and tissues. Unlike conventional MRI, the open version features a more spacious and open design, which is more comfortable for patients, especially those who are claustrophobic or overweight.
✔️ Benefits of Open MRI
- Patient Comfort: The open design reduces feelings of confinement and anxiety, offering a more pleasant experience for the patient.
- Improved Access: Ideal for people who are overweight or who need greater positioning flexibility during the exam.
- Image Quality: Provides high-quality images that are crucial for an accurate diagnosis.
- Versatility: Can be used to evaluate various parts of the body, including the brain, spine, joints, and internal organs.
What does an MRI detect?
An MRI detects abnormalities in soft tissues, organs, blood vessels, and the central nervous system.
What is the difference between a CT scan and an MRI?
The difference between a CT scan and an MRI is that a CT scan uses X-rays to obtain images primarily of bony structures, while an MRI uses magnetic fields to better visualize soft tissues.
How to Prepare for an Open MRI?
Before the exam, it is recommended to:
Tell your doctor: If you have metal implants, pacemakers, or other medical devices, you should tell your doctor, as they may interfere with the exam.
Fasting: In some cases, you may be asked to avoid eating or drinking for several hours before the procedure.
Comfortable clothing: Wear comfortable clothing and avoid clothing with metal elements. In many cases, you will be provided with a gown to change into.
What to Expect During the Procedure?
- Entering the Exam Room: You will lie on a table that slides into the open MRI scanner.
- Stay still: It’s crucial to stay as still as possible to get clear images. You can breathe normally, but avoid sudden movements.
- Length: The exam usually takes 30 to 60 minutes, depending on the body part being evaluated.
- Noise: The equipment may make loud noises during the exam. You will be provided with earplugs or headphones to minimize discomfort.
What to do after the MRI test?
Once the exam is complete, you can resume your normal activities immediately. The radiologist will analyze the images and send a detailed report to your doctor, who will discuss the results and next steps with you.
Difference between Non-Contrast and Contrast-Enhanced MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce detailed images of the body’s organs and tissues.
There are two main types of MRI studies: contrast-enhanced and non-contrast.
Here are the differences between the two:
Non-contrast MRI
A non-contrast MRI is performed without the injection of contrast agents into the body.
- Procedure: The patient lies on the MRI table and is placed in the scanner.
The scanner uses magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of the inside of the body. - Indications: Used to obtain detailed images of internal structures without the need for contrast enhancement of tissues.
Indicated to evaluate the brain, spinal cord, joints, bones, and internal organs without suspicion of very specific or small injuries. - Advantages: Does not involve the injection of chemicals into the body, which reduces the risk of allergic reactions or side effects.
It is safer for people with kidney problems or allergies to contrast agents.
Contrast-Enhanced MRI
A contrast-enhanced MRI involves the injection of a contrast agent (usually gadolinium) into the bloodstream before or during the study.
- Procedure: Similar to non-contrast MRI, but includes the injection of contrast.
The contrast agent enhances the visibility of certain structures and tissues by altering the way they respond to the magnetic field and radio waves. - Indications: Used when greater detail is needed to evaluate tumors, inflammation, infections, vascular problems, and other pathologies.
It is useful for observing the blood-brain barrier, tissue perfusion, and vascularity of tumors. - Advantages: Provides clearer and more detailed images of certain tissues and structures.
Helps to better detect and characterize lesions, as the contrast highlights abnormal areas that may not be visible on a non-contrast MRI. - Disadvantages: It may not be suitable for all patients, especially those with severe kidney failure or allergies to gadolinium.
Some people may experience minor side effects, such as nausea or a warm feeling after the injection.
Digital Radiology
What is Digital Radiology
Digital radiology, or X-rays, is one of the most modern types of radiography. It uses digital sensors composed of layers that capture images, allowing us to see the inside of the body.
What are its functions
It enables the performance of an internal diagnosis, giving the radiologist the opportunity to understand the patient’s condition using instruments or probes.
This allows for the execution of MRI scans, mammograms, CT scans, X-rays, and bone densitometry.
Its benefits
Digital radiology offers a visual guide that projects cerebrovascular and heart diseases present in the patient.
It becomes a crucial tool for correctly following a treatment plan.
It also helps detect conditions such as cancer.

 We have many English speaking patients!
We have many English speaking patients!